血管平滑肌细胞(VSMCs)异常增殖和迁移在高血压血管重构中发挥关键作用[1-2]。内皮素-1(ET-1)在VSMCs中表现出促有丝分裂、肥大反应的作用[3-4],还参与高血压、心力衰竭和动脉粥样硬化等多种心血管疾病的病理过程[5-8]。抑制ET-1诱导的VSMCs异常增殖和迁移,可以抑制上述病理进程[9]。anoctamin-1(ANO1或TMEM16A)是一种钙激活氯通道,涉及腺上皮分泌、平滑肌收缩、心肌生物电和感觉信号转导等多项功能[10-11],在VSMCs中广泛表达[12],在自发性高血压大鼠和肺动脉高压大鼠中参与血管重构的发生[13-14]。本研究通过检测增殖细胞核抗原(PCNA),进一步观察ANO1特异性抑制剂T16Ainh-A01(A01)对ET-1诱导的细胞增殖的影响,通过检测α-平滑肌肌动蛋白(α-SMA)和骨桥蛋白(OPN)探讨A01可能的作用机制。
1 材料与方法 1.1 试剂与仪器ET-1购自上海AbMole公司,A01购自Sigma公司,PCNA抗体由Cell Signaling Technology公司提供,α-SMA和OPN抗体购自Abcam公司,β-actin抗体由北京博奥森公司提供,DMEM高糖培养液购自Gibco公司,胎牛血清购自美国BI公司,BCA蛋白测定试剂盒由上海Thermo公司提供,RIPA裂解液购自上海碧云天生物科技研究所,其他试剂均为国产分析纯。ET-1使用无菌水配成1 mmol/L的母液,A01用二甲基亚砜(DMSO)配成10~20 mmol/L的母液,使用前均用DMEM培养液稀释到终浓度。实验所用仪器包括CO2培养箱、超净工作台、Eppendorf高速离心机、37 ℃恒温孵育箱、多功能酶标仪以及Western显影仪等。
1.2 VSMCs的原代培养选用体质量70~100 g(大约3周龄)的Wistar大鼠,以400 mg/kg水合氯醛腹腔注射麻醉。用体积分数为0.75的乙醇浸泡消毒后,置于无菌超净工作台内。迅速分离胸主动脉,将动脉放入加DMEM培养液的玻璃皿中,去除血管外结缔组织,沿中线剪开,用弯镊子轻柔刮下内皮,用眼科剪将其剪成大小约1 mm3小块,平铺于50 mL培养瓶底部,加入含有体积分数0.20胎牛血清的DMEM高糖培养液4~5 mL,直立放入培养箱内,5~6 h后翻瓶,培养1周左右,在显微镜下可看到贴壁组织块周围有VSMCs爬出,细胞融合达到60%~70%时进行传代,选择第5~8代生长良好的细胞进行后续实验。
1.3 实验分组将VSMCs分为对照组(A组,无药物处理)、ET-1组(B组,用1 nmol/L ET-1处理)、ET-1+A01组(C组,同时加入1 nmol/L ET-1和20 μmol/L A01)、A01组(D组,用20 μmol/L A01处理),药物处理24 h后提取蛋白进行检测。
1.4 Western blot检测药物处理结束后用RIPA裂解液提取蛋白,用BCA试剂盒测定蛋白浓度。所有样品上样量均为20 μg,经SDS-PAGE电泳后转移至PVDF膜上。用含100 g/L脱脂奶粉的TBST封闭1 h后,分别加入抗PCNA(1∶2 000)、α-SMA(1∶30 000)、OPN(1∶1 000)和β-actin(1∶8 000)抗体等一抗,4 ℃摇床孵育过夜。以TBST洗膜3次后,加入HRP标记的二抗,室温孵育1 h,ECL发光液显影,用Image J软件分析条带的灰度值。实验重复5次。
1.5 统计学分析所得数据以x±s表示,应用SPSS 22.0软件采用2×2析因设计的方差分析进行统计学分析,P<0.05认为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 A01对PCNA蛋白表达的影响析因设计的方差分析显示,ET-1的主效应明显(F=16.755,P<0.01),A01的主效应无统计学意义(F=3.187,P>0.05),ET-1和A01之间有交互作用(F=9.028,P<0.01)。单独效应分析显示:与对照组比较,ET-1组PCNA蛋白表达明显上调(F=25.190,P<0.01);与ET-1组比较,ET-1+A01组PCNA蛋白表达明显下降(F=11.472,P<0.01);单独使用A01对PCNA蛋白表达没有明显影响(F=0.743,P>0.05)。提示单独应用ET-1可明显促进PCNA蛋白的表达,ET-1的作用可被A01所拮抗。见图 1、表 1。
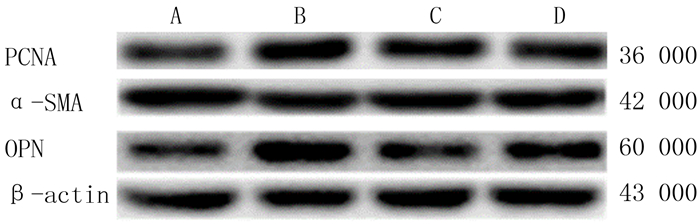 |
| A:对照组;B:ET-1组;C:ET-1+A01组;D:A01组。 图 1 各组PCNA、α-SMA、OPN蛋白表达的Western blot检测 |
| 表 1 各组PCNA、α-SMA、OPN蛋白表达的比较(n=5,x±s) |
|
|
析因设计的方差分析显示,ET-1的主效应明显(F=10.306,P<0.01),A01主效应无统计学意义(F=3.853,P>0.05),两种药物之间有交互作用(F=9.612,P<0.01)。单独效应分析显示:与对照组比较,ET-1组α-SMA蛋白表达明显下降(F=19.912,P<0.01);与ET-1组比较,ET-1+A01组α-SMA蛋白表达明显上调(F=12.818,P<0.01);单独使用A01对α-SMA蛋白表达没有明显影响(F=0.647,P>0.05)。提示单独应用ET-1可使α-SMA蛋白水平升高,应用A01可阻断ET-1的作用。见图 1、表 1。
2.3 A01对OPN蛋白表达的影响析因设计的方差分析显示,ET-1和A01的主效应均无统计学意义(F=1.940、2.755,P>0.05),两种药物之间有交互作用(F=9.201,P<0.01)。单独效应分析显示:与对照组比较,ET-1组OPN蛋白表达明显上调(F=9.795,P<0.01);与ET-1组比较,ET-1+A01组OPN蛋白表达明显下降(F=11.013,P<0.01);单独使用A01对OPN蛋白表达没有明显影响(F=0.943,P>0.05)。提示单独应用ET-1可使OPN蛋白水平升高,应用A01可阻断ET-1的作用。见图 1、表 1。
3 讨论长期的高血压可导致血管结构和功能的改变,又称血管重构,血管重构和高血压的发展及重要靶器官损伤密切相关[15-16]。VSMCs作为血管壁的主体细胞,其异常的增殖迁移在高血压血管重构中发挥重要作用。体内多种因素,如血流动力学改变、血管活性物质(如血管紧张素Ⅱ、ET-1)、炎症因子和生长因子(如成纤维细胞生长因子、表皮细胞生长因子等),均与VSMCs功能异常密切相关[17-20]。
ET-1是内皮细胞分泌的最重要的血管活性物质,具有很强的缩血管效应;ET-1也是一种有丝分裂原,在维持血管功能稳态中具有重要作用[3]。通常认为,ET-1诱导VSMCs异常增殖迁移与其结合ETA受体后导致胞内钙增加、AKT和ERK信号通路激活等有关[21-22]。
最近研究发现,钙激活氯通道ANO1也是参与VSMCs功能调控的重要调控因子[13, 23-25]。ANO1激活可诱导VSMCs收缩,而抑制其功能性表达则通过舒张血管降低血压[23-24]。在自发性高血压大鼠中,VSMCs上ANO1功能性高表达促进高血压形成[13]。此外,ANO1还可以作为一种细胞增殖调节因子参与VSMCs增殖,促进血管重构和降低血管弹性[26-28]。
我们的前期研究发现,ET-1能够明显上调VSMCs的ANO1表达[15]。本研究利用ANO1特异性抑制剂A01进一步探讨了ANO1高表达是否参与了ET-1诱导的VSMCs增殖。PCNA是DNA合成中重要的辅助因子,也是检测细胞增殖最常用的指标。本研究PCNA检测结果表明,A01可明显抑制ET-1诱导的VSMCs增殖。
正常的VSMCs呈现出高度分化、低增殖能力的收缩表型,其作用是调节血管壁张力及维持组织血流量,其标志性蛋白主要为α-SMA和平滑肌22α等;合成型VSMCs呈低分化,可分泌大量细胞外基质,参与血管壁形成、损伤修复等,其标志性蛋白主要为OPN。VSMCs可由收缩型转化为合成型,后者具有强大的增殖迁移能力从而促进血管重构的发生[29-30]。为进一步探讨A01的作用机制,本实验又检测了SMA和OPN蛋白的表达。结果显示,ET-1处理细胞24 h后,α-SMA表达降低而OPN表达升高,即ET-1能够诱导VSMCs由收缩型转化为合成型,促进细胞增殖,而应用A01可明显阻断上述变化。根据已有的研究文献,我们推测A01对细胞表型的调控可能与它抑制PI3K/AKT和ERK信号通路有关[26-27]。
综上所述,ANO1特异性抑制剂A01对ET-1诱导的VSMCs增殖有明显的抑制作用,其作用可能与A01抑制ET-1诱导的细胞表型转换有关,这为ET-1引发的高血压、心力衰竭和动脉粥样硬化等多种心血管疾病的治疗提供了依据。
| [1] |
RIZZONI D, AGABITI-ROSEI E. Structural abnormalities of small resistance arteries in essential hypertension[J]. Internal and Emergency Medicine, 2012, 7(3): 205-212. DOI:10.1007/s11739-011-0548-0 |
| [2] |
ZHANG F, GUO X Q, XIA Y P, et al. An update on the phenotypic switching of vascular smooth muscle cells in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis[J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 2021, 79(1): 6. |
| [3] |
JANKOWICH M, CHOUDHARY G. Endothelin-1 levels and cardiovascular events[J]. Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine, 2020, 30(1): 1-8. DOI:10.1016/j.tcm.2019.01.007 |
| [4] |
CARBONE F, MONTECUCCO F, SAHEBKAR A. Editorial commentary: promising findings on the role of endothelin-1 and related peptides in primary cardiovascular prevention[J]. Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine, 2020, 30(1): 9-10. DOI:10.1016/j.tcm.2019.02.006 |
| [5] |
LIU R Q, YUAN T Y, WANG R R, et al. Insights into endothelin receptors in pulmonary hypertension[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(12): 10206. DOI:10.3390/ijms241210206 |
| [6] |
CAI Z Y, GONG Z, LI Z Q, et al. Vascular extracellular matrix remodeling and hypertension[J]. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 2021, 34(10): 765-783. |
| [7] |
EROGLU E, KOCYIGIT I, LINDHOLM B. The endothelin system as target for therapeutic interventions in cardiovascular and renal disease[J]. Clinica Chimica Acta; International Journal of Clinical Chemistry, 2020, 506: 92-106. DOI:10.1016/j.cca.2020.03.008 |
| [8] |
ZHAI M, GONG S Y, LUAN P P, et al. Extracellular traps from activated vascular smooth muscle cells drive the progression of atherosclerosis[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 7500. DOI:10.1038/s41467-022-35330-1 |
| [9] |
MOORHOUSE R C, WEBB D J, KLUTH D C, et al. Endothelin antagonism and its role in the treatment of hypertension[J]. Current Hypertension Reports, 2013, 15(5): 489-496. DOI:10.1007/s11906-013-0380-1 |
| [10] |
LIU Y N, LIU Z T, WANG K W. The Ca2+-activated chloride channel ANO1/TMEM16A: an emerging therapeutic target for epithelium-originated diseases?[J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2021, 11(6): 1412-1433. DOI:10.1016/j.apsb.2020.12.003 |
| [11] |
DULIN N O. Calcium-activated chloride channel ANO1/TMEM16A: regulation of expression and signaling[J]. Frontiers in Physiology, 2020, 11: 590262. DOI:10.3389/fphys.2020.590262 |
| [12] |
ZENG J W, CHEN B Y, LV X F, et al. Transmembrane member 16A participates in hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis by facilitating mitochondria-dependent pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells[J]. British Journal of Pharmacology, 2018, 175(18): 3669-3684. DOI:10.1111/bph.14432 |
| [13] |
WANG B X, LI C L, HUAI R T, et al. Overexpression of ANO1/TMEM16A, an arterial Ca2+-activated Cl- channel, contributes to spontaneous hypertension[J]. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology, 2015, 82: 22-32. DOI:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2015.02.020 |
| [14] |
XIE J Y, LIU W Y, LV W J, et al. Transmembrane protein 16A/anoctamin 1 inhibitor T16Ainh-A01 reversed monocrotaline-induced rat pulmonary arterial hypertension[J]. Pulmonary Circulation, 2020, 10(4): 2045894020946670. |
| [15] |
GAO Q N, XU L, CAI J. New drug targets for hypertension: a literature review[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta Molecular Basis of Disease, 2021, 1867(3): 166037. DOI:10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.166037 |
| [16] |
BROWN I A M, DIEDERICH L, GOOD M E, et al. Vascular smooth muscle remodeling in conductive and resistance arteries in hypertension[J]. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 2018, 38(9): 1969-1985. DOI:10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311229 |
| [17] |
LAMB F S, CHOI H, MILLER M R, et al. TNFα and reactive oxygen signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells in hypertension and atherosclerosis[J]. American Journal of Hypertension, 2020, 33(10): 902-913. DOI:10.1093/ajh/hpaa089 |
| [18] |
HUMPHREY J D. Mechanisms of vascular remodeling in hypertension[J]. American Journal of Hypertension, 2021, 34(5): 432-441. DOI:10.1093/ajh/hpaa195 |
| [19] |
SHI J, YANG Y, CHENG A Y, et al. Metabolism of vascular smooth muscle cells in vascular diseases[J]. American Journal of Physiology Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 2020, 319(3): H613-H631. DOI:10.1152/ajpheart.00220.2020 |
| [20] |
BASATEMUR G L, JØRGENSEN H F, CLARKE M C H, et al. Vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis[J]. Nature Reviews Cardiology, 2019, 16(12): 727-744. DOI:10.1038/s41569-019-0227-9 |
| [21] |
TIAN X Y, ZHANG Q Y, HUANG Y Q, et al. Endothelin-1 downregulates sulfur dioxide/aspartate aminotransferase pathway via reactive oxygen species to promote the proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells[J]. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2020, 2020: 9367673. |
| [22] |
HEINZE C, SENIUK A, SOKOLOV M V, et al. Disruption of vascular Ca2+-activated chloride currents lowers blood pressure[J]. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 2014, 124(2): 675-686. DOI:10.1172/JCI70025 |
| [23] |
OH U, JUNG J. Cellular functions of TMEM16/anoctamin[J]. Pflugers Archiv: European Journal of Physiology, 2016, 468(3): 443-453. DOI:10.1007/s00424-016-1790-0 |
| [24] |
JACKSON W F. Calcium-dependent ion channels and the regulation of arteriolar myogenic tone[J]. Frontiers in Physiology, 2021, 12: 770450. DOI:10.3389/fphys.2021.770450 |
| [25] |
SUZUKI T, YASUMOTO M, SUZUKI Y, et al. TMEM16A Ca2+-activated Cl- channel regulates the proliferation and migration of brain capillary endothelial cells[J]. Molecular Pharmacology, 2020, 98(1): 61-71. |
| [26] |
JI Q S, GUO S, WANG X Z, et al. Recent advances in TMEM16A: structure, function, and disease[J]. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 2019, 234(6): 7856-7873. |
| [27] |
ZHANG X, ZHANG G H, ZHAO Z J, et al. Cepharanthine, a novel selective ANO1 inhibitor with potential for lung adenocarcinoma therapy[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta Molecular Cell Research, 2021, 1868(12): 119132. |
| [28] |
GUO S S, ZHANG L N, LI N. ANO1: more than just calcium-activated chloride channel in cancer[J]. Frontiers in Oncology, 2022, 12: 922838. |
| [29] |
CLÉMENT M, CHAPPELL J, RAFFORT J, et al. Vascular smooth muscle cell plasticity and autophagy in dissecting aortic aneurysms[J]. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 2019, 39(6): 1149-1159. |
| [30] |
CAO G M, XUAN X Z, HU J, et al. How vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype switching contributes to vascular disease[J]. Cell Communication and Signaling, 2022, 20(1): 180. |
 2024, Vol. 60
2024, Vol. 60

